As the world becomes increasingly connected and reliant on mobile devices, the threat of mobile malware is becoming more prevalent. One of the most dangerous mobile malware currently in circulation is Roaming Mantis.
This malware can infect Android smartphones and tablets, redirect iOS devices to a phishing site, and run a crypto-mining script on desktops and laptops.
In this article, I will explore how Roaming Mantis works and provide tips on how to protect yourself from this mobile malware.
The Spread of Roaming Mantis
Initially, Roaming Mantis was targeting users in Japan, Korea, China, India, and Bangladesh. However, it quickly learned 12 more languages and spread across the globe. Its creators use compromised routers to infect Android devices and redirect iOS devices to a phishing site.
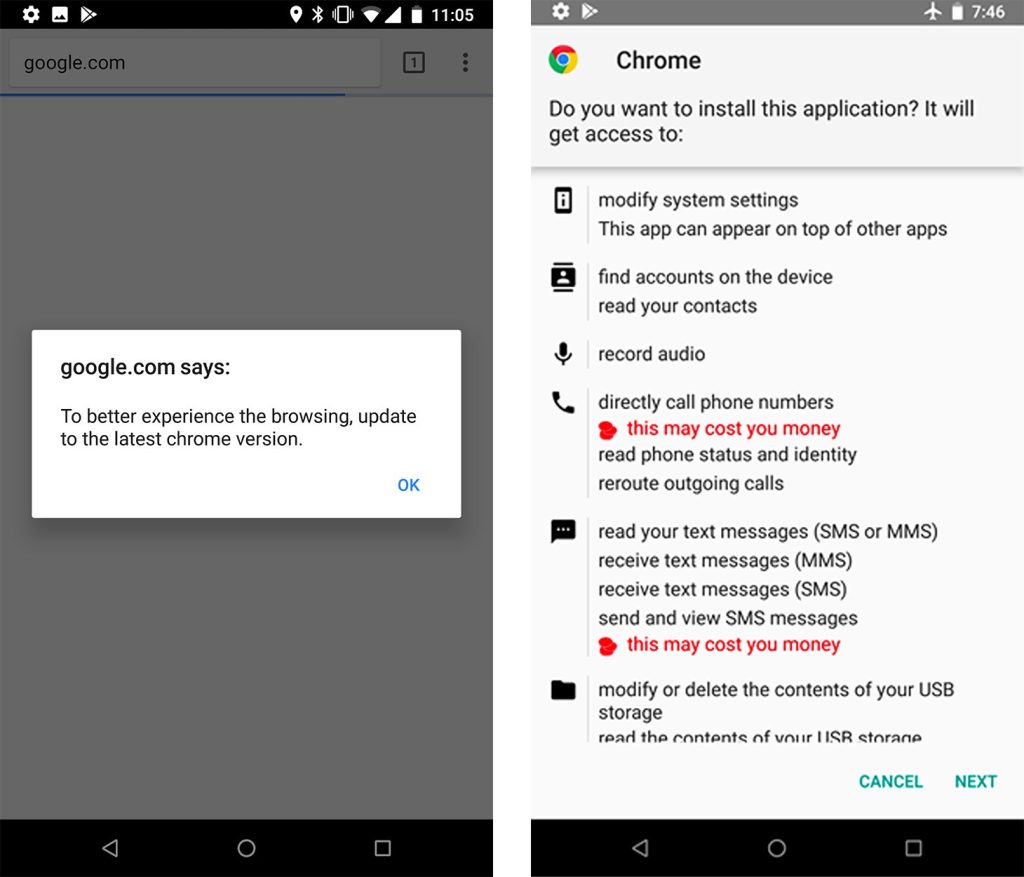
Roaming Mantis hijacks the DNS of compromised routers, making it difficult for users to detect that something is wrong. When the user accesses the malicious site, they are prompted to refresh their browser and download a malicious application known as chrome.apk or Facebook.apk.
Once the user installs the malicious application, Roaming Mantis requests many permissions, including access to account information, the ability to send and receive SMS, audio recording, file access, and display its window for others.
If the user considers the “browser update” to be legitimate, they will likely grant these permissions without even reading the list.
How Roaming Mantis Infects Android Devices
Roaming Mantis on Android devices is a significant threat as it can access personal information and steal Google accounts. After installing the malware, Roaming Mantis uses the right to access the account list to find out which Google account is used on the device.
Then, the user receives a message stating that something is wrong with the account and that they need to log in again.
The user is directed to a page that encourages them to enter their name and date of birth.
Roaming Mantis uses this data, along with SMS permissions that grant access to one-time codes required for two-factor authentication, to steal Google accounts.
How Roaming Mantis Infects iOS Devices
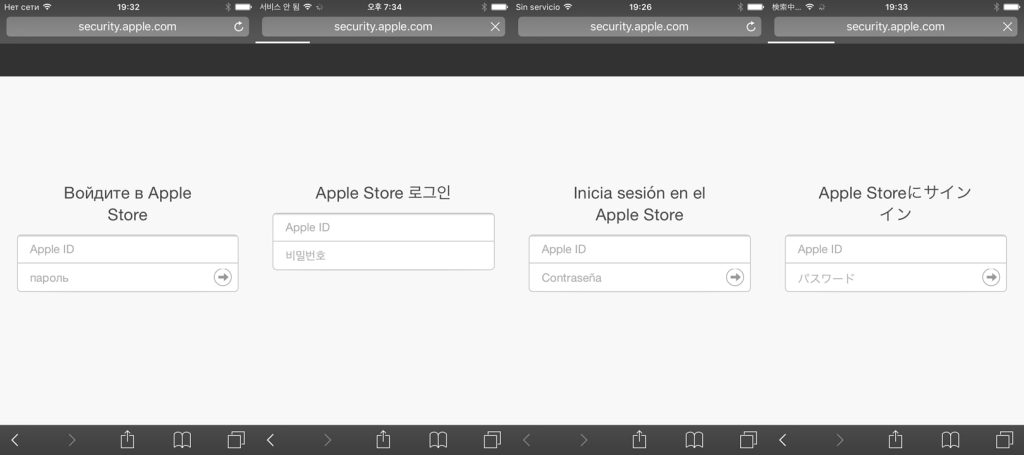
Roaming Mantis on iOS devices is a completely different scenario. The user is directed to a phishing page that prompts them to log in to the App Store immediately. The address bar shows the address security.apple.com, giving the phishing page credibility.
The user is then prompted to enter their bank card number, which the cybercriminals can steal.
Protecting Yourself from Roaming Mantis
Now that you understand how Roaming Mantis works, it is crucial to protect yourself from this mobile malware. Here are some tips to keep in mind:
- Keep your devices updated with the latest security patches and software updates.
- Be cautious when downloading and installing applications, especially from unknown sources.
- Use strong passwords and enable two-factor authentication for all your online accounts.
- Use a trusted antivirus solution that can detect and remove mobile malware.
- Delegate your mobile, desktop, and server cyber security to experts.
If you have an Android device, the best way to avoid becoming infected with Roaming Mantis is to keep your device and apps up to date with the latest security patches. It’s also important to only download apps from trusted sources, such as the Google Play Store.
If you receive a suspicious message or see any signs that your device might be infected, such as unexpected pop-ups or slow performance, it’s important to act quickly and run a malware scan on your device.